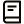
Warm Tip :
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Raymond Mill Machine and Ball Mill are two very common Industrial Grinding Equipment. They differ in structure, working principle, applicable materials and scenarios.
Below, VEST Machinery analyzes the differences between Raymond Mill and Ball Mill Grinder from 6 aspects. I hope it will be helpful for you when purchasing a grinding mill.
1. Structure and Working Principle
| Comparison Items | Raymond Mill | Ball Mill |
| Structural Form | The vertical structure consists of the main machine (grinding roller, grinding ring), analyzer, fan, cyclone separator, etc. | Horizontal drum structure, with grinding media (steel balls or ceramic balls) installed in the drum. |
| Crushing Principle | Roller centrifugal compaction: Rollers rotate and compact the material, while analyzers separate the fine powder. | Impact and grinding: The rotation of the cylinder drives the grinding media to fall, crushing the material through impact and friction. |
| Grading Method | The built-in analyzer performs real-time sorting and the fine powder is discharged directly. | External screening equipment or discharge particle size control (such as overflow ball mill) is required. |
| System Complexity | Highly integrated, with built-in grading and powder collection system. | The structure is simple, but it needs matching sorting equipment (such as spiral classifier, vibrating screen). |

2. Comparison of Crushing Performance
| Comparison Items | Raymond Mill | Ball Mill |
| Product Fineness | Fineness range: 80-600 mesh (some can reach 2500 mesh), with uniform particle size. | The fineness is relatively coarse, usually 50-300 mesh, and multiple grinding or closed-circuit sorting is required to increase the fineness. |
| Production Efficiency | Small and medium capacity (1-30 t/h), suitable for continuous production of fine powders. | Large production capacity (up to hundreds of t/h), suitable for large-scale coarse crushing or wet grinding. |
| Energy Consumption | Low specific energy consumption (integrated classification, reduced over-crushing). | High energy consumption (long-term operation, large medium friction loss). |
| Noise and Vibration | The noise level is low (about 75-85 decibels). | The noise is loud (over 90 decibels) and the vibration |

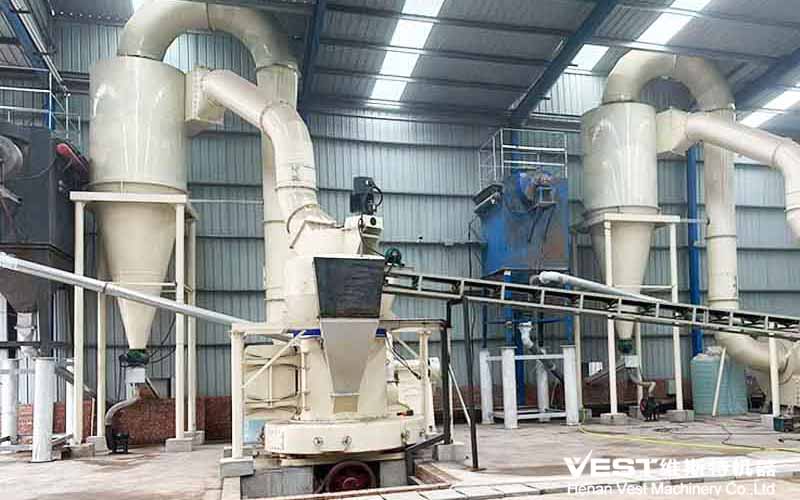
3. Applicable material characteristics
| Comparison Items | Raymond Mill | Ball Mill |
| Material Hardness | Suitable for low to medium hardness materials (Mohs hardness ≤ 7), such as limestone, calcite, talc, etc. | Suitable for materials with high hardness (such as metal ores, quartz sand, etc., Mohs hardness ≤ 9). |
| Material Humidity | It is required to be dry (moisture content ≤ 6%), as wet materials are prone to clogging. | It can process wet materials (wet ball milling) and is suitable for materials with high moisture content. |
| Material Viscosity | Not suitable for sticky materials (easy to stick to grinding rollers and grinding rings). | Slightly sticky materials can be processed by adjusting the medium and speed. |
4. Application Fields
| Field | Typical Applications of Raymond Mill | Typical Applications of Ball Mill |
| Non-Metallic Minerals | Processing of fine powders such as limestone, barite, gypsum, bentonite, kaolin, etc. | Coarse crushing or pre-grinding of quartz sand, feldspar, fluorite and other ores. |
| Metal Minerals | Not suitable for high hardness metal ores. | Crushing and fine grinding of metal ores such as iron ore, copper ore, gold ore, etc. |
| Chemicals and Building Materials | Preparation of coatings, rubber fillers, desulfurized lime powder, etc. | Cement clinker grinding, ceramic raw material preparation, silicate product production. |
| Other Industries | Medical and food grade fine powder (stainless steel material required). | Metallurgical ore dressing, coal powder preparation (wet or dry process), solid waste treatment. |
5. Summary of Fdvantages and Disadvantages
| Equipment | Advantage | Shortcoming |
| Raymond Mill | 1). High fineness and uniform particle size; 2). High degree of automation and energy saving; 3). Small footprint and easy maintenance | 1). Not suitable for high hardness, high humidity and sticky materials; 2). The production capacity is relatively low. |
| Ball Mill | 1). Strong adaptability, able to handle a variety of materials; 2). Large production capacity, suitable for large-scale production; 3). Can be operated wet or dry | 1). High energy consumption and loud noise; 2). Fineness control depends on sorting equipment; 3). High maintenance cost (media wear). |
6. Selection Suggestions
1)Situation for Choosing Raymond Mill:
The target fineness requirement is high (above 80 mesh), and the material is dry and of moderate hardness.
Small and medium-scale production, pursuit of low energy consumption and automated control.
Typical scenarios: non-metallic mineral powder making, coating fillers, power plant desulfurization, etc.
2)Selection of Ball Mill
Processing high hardness ores or requiring wet grinding (such as mineral processing).
Large-scale continuous production has relatively loose requirements on fineness (50-300 mesh).
Typical scenarios: cement production, metal ore dressing, ceramic raw material preparation, etc.
 Phone/Wechat/Whatsapp:+86-19515530562
Phone/Wechat/Whatsapp:+86-19515530562
 Email:crusher@hn-vest.com
Email:crusher@hn-vest.com
 Message
Message Online
Online